The cost of aged care continues to be a critical topic of concern, particularly in Perth where the funding and management of services play a central role in ensuring sustainable, high-quality outcomes. Aged care expenditure is shaped by a combination of individual needs, systemic considerations, and broader socio-economic influences.
This article examines the key factors impacting aged care costs in Perth, offering insights into the operational and environmental elements that influence overall expenditure—without focusing on specific financial figures.
Aged Care That Balances Tradition & Quality
Hellenic Aged Care, a respected aged care home in Perth, delivers a unique combination of traditional Hellenic values and contemporary care practices. More than a facility, it offers residents a culturally enriched environment built around respect, community, and personal wellbeing.
With a dedicated team of qualified professionals, Hellenic Aged Care provides comprehensive services including residential aged care, dementia support, and palliative care. This approach ensures that each resident receives care aligned with their physical, emotional, and cultural needs—promoting dignity and comfort in their later years.
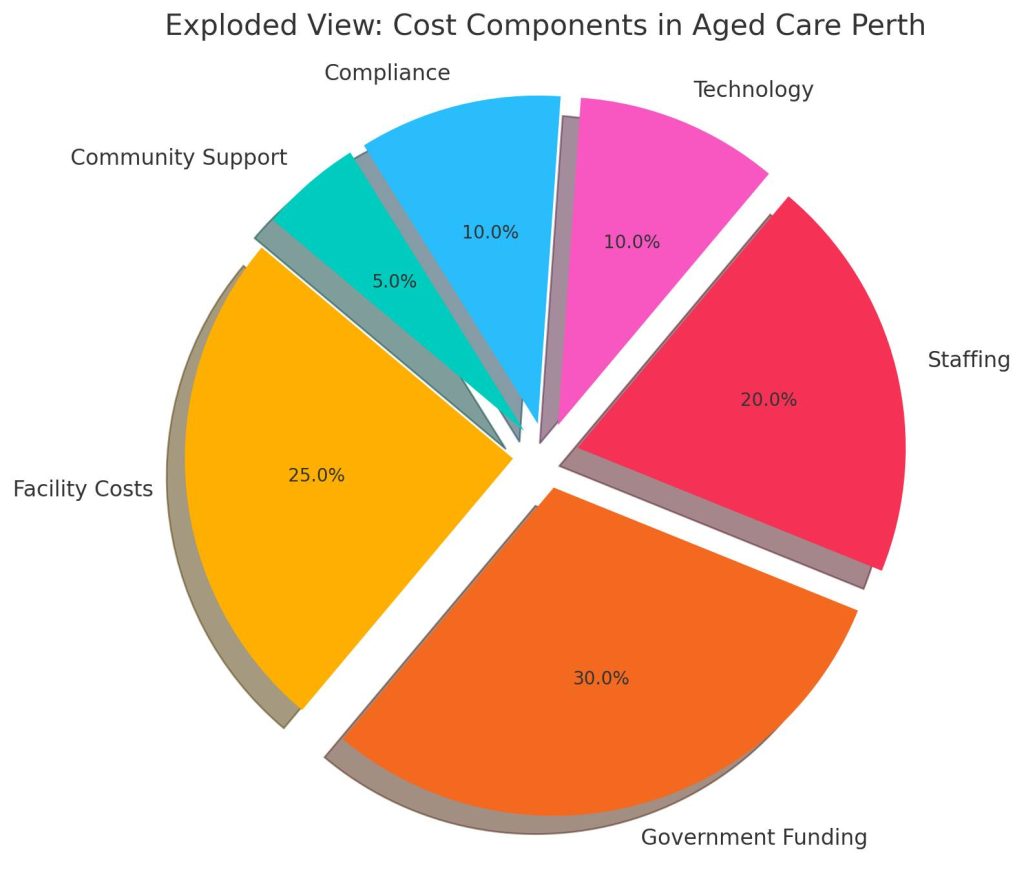
Key Cost Influencers in Aged Care
Level of Care Required
The primary driver of aged care costs is the level of assistance an individual requires. Residents with complex medical conditions or reduced mobility may need specialist care services such as ongoing nursing support, physical therapy, or dementia care. These specialised services are typically more resource-intensive compared to standard assistance with daily living tasks like hygiene, meals, or mobility.
Type of Aged Care Facility
The cost structure varies significantly between care options. Full-service residential facilities—particularly those offering 24/7 care—carry higher operational costs due to staffing, infrastructure, and regulatory obligations. In contrast, home-based care or community-supported services may offer a more cost-effective alternative, especially for those with lower care needs. Factors such as the quality of amenities, staff expertise, and resident-to-carer ratios further influence pricing across different aged care settings.
Geographic Location
In Perth, aged care costs are also shaped by the facility’s location. Regions with higher property values or living expenses often reflect these costs in aged care pricing. Additionally, areas with limited service availability may face higher charges due to increased transport requirements or reduced competition, especially in remote or outer suburban zones.
Government Funding & Subsidies
Government contributions play a significant role in mitigating aged care expenses. Eligibility for subsidies and the extent of available support can vary depending on income, assets, and care needs. Policy changes and reforms in funding frameworks can also impact the cost and accessibility of aged care services in Perth over time.
Integration with Healthcare Services
Aged care becomes more cost-effective when integrated effectively with the broader healthcare system. Coordination between hospitals, general practitioners, and aged care providers ensures seamless transitions, reduces duplication of services, and maximises the use of available resources.
Use of Technology
Technological advancements such as telehealth, electronic health monitoring, and automated medication management contribute to improved service efficiency and safety. Innovations in facility management systems can also streamline operations, potentially reducing staffing and administrative overheads.
Workforce Capability
A skilled workforce is fundamental to maintaining care quality. Investment in ongoing training and staff development enhances service standards and operational efficiency. Workforce planning that aligns staffing levels with resident needs can also help control labour-related expenses.
Regulatory Compliance
Adherence to industry standards and regulations is essential but adds to operational costs. Regular audits, infrastructure upgrades, staff training, and compliance systems are necessary investments to ensure safety and quality of care, but they also contribute to overall expenditure.
Community & Volunteer Support
Community engagement and volunteerism can provide non-financial support to aged care facilities. Volunteers often contribute to lifestyle programs, companionship, and general assistance, thereby supplementing paid services and adding value to resident care without increasing costs.
Economic Conditions
Wider economic trends, including inflation, labour market changes, and government budget priorities, influence funding allocations and private investment in aged care. Economic downturns can constrain financial resources, while strong growth may allow for improved funding and service expansion.
Conclusion
Understanding the diverse factors influencing aged care expenditure allows stakeholders to make informed decisions that support both financial viability and high-quality outcomes. From policy frameworks to workforce investment, every component plays a role in shaping the aged care landscape.
As aged care in Perth continues to evolve, a strategic approach—balancing quality, sustainability, and affordability—will be essential. With services like Hellenic Aged Care leading by example, there is clear potential for aged care Perth to meet the complex and changing needs of its ageing population.