As Perth’s population ages, ensuring high-quality health outcomes in aged care facilities is essential to maintaining the well-being of elderly residents. The healthcare services provided within these facilities have a direct impact on the quality of life, life expectancy, chronic illness management, and hospitalisation rates. In this statistical review, we will assess the current health outcomes in Aged Care Perth, examining life expectancy, chronic illness management, and hospitalisation rates among residents.
Life Expectancy in Perth’s Aged Care Facilities
The life expectancy of residents in aged care facilities in Perth is slightly lower than that of the general population. Nationally, Australians have an average life expectancy of 83.4 years. However, elderly individuals in aged care facilities tend to have more complex health needs, which can lead to a reduction in their overall life expectancy compared to those living independently.
A recent report indicates that the average length of stay in aged care facilities is approximately 2.5 years, reflecting the advanced age and frailty of residents by the time they enter care. Perth mirrors these national trends, with many residents requiring a high level of medical support during the final years of their lives.
Chronic Illness Management
Chronic illness management plays a crucial role in determining the quality of life for aged care residents. According to a recent survey, around 80% of aged care residents in Perth are managing at least one chronic condition, such as dementia, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, or arthritis. Dementia, in particular, affects nearly 60% of aged care residents across Australia, with similar rates observed in Perth facilities.
The management of these chronic conditions significantly influences health outcomes. Effective chronic illness management in Aged Care Perth facilities involves a combination of medication, specialised care, and ongoing monitoring. However, there are disparities in the quality of care across facilities. Some homes have established stronger protocols for managing chronic diseases, which leads to better resident outcomes, while others may struggle with staffing and resource constraints that impact the level of care provided.
Hospitalisation Rates Among Aged Care Residents
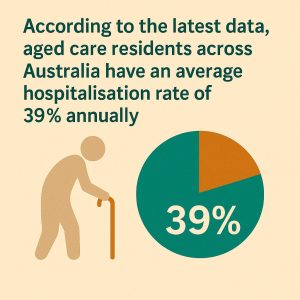
Hospitalisation rates are a key indicator of health outcomes in aged care facilities. A high rate of hospital admissions can indicate inadequate in-house care or poor chronic disease management. According to the latest data, aged care residents across Australia have an average hospitalisation rate of 39% annually. In Perth, this figure is similar, with hospital admissions frequently related to falls, respiratory illnesses, and complications from chronic diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular conditions.
Preventable hospitalisations, such as those for infections, injuries, and falls, remain a significant concern. These hospitalisations not only place a strain on the healthcare system but also impact the well-being of the residents. There is a growing push within Aged Care Perth facilities to invest in preventive measures, such as fall prevention programmes and better infection control, to reduce unnecessary hospital visits.
Improving Health Outcomes in Perth’s Aged Care Facilities
While Perth’s aged care facilities are working to improve health outcomes, several key areas need further development. Investment in staff training, chronic disease management, and preventive care can significantly reduce hospitalisations and improve the quality of life for residents.
One promising development is the increasing use of digital health monitoring systems, which enable more proactive management of chronic conditions. Some facilities are also partnering with local healthcare providers to ensure that residents have better access to specialised care without the need for frequent hospital admissions.
Conclusion
The health outcomes in Aged Care Perth facilities are shaped by multiple factors, including life expectancy, chronic illness management, and hospitalisation rates. While aged care facilities in Perth are making strides in managing the complex needs of their residents, there is still room for improvement. Investing in preventive care, staff development, and chronic disease management protocols can help enhance the quality of life for Perth’s ageing population. Ultimately, ensuring that aged care residents receive the highest standard of care is essential for promoting longer, healthier lives in Perth’s aged care facilities.